| Feb 07, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) For the primary time, researchers have recorded dwell and in atomic element what occurs to the fabric in an asteroid affect. The workforce of Falko Langenhorst from the College of Jena and Hanns-Peter Liermann from DESY simulated an asteroid affect with the mineral quartz within the lab and pursued it in gradual movement in a diamond anvil cell, whereas monitoring it with DESY’s X-ray supply PETRA III.
|
|
The commentary reveals an intermediate state in quartz that solves a decades-old thriller concerning the formation of attribute lamellae in quartz hit by an asteroid. Quartz is ubiquitous on the Earth’s floor, and is, for instance, the foremost constituent of sand. The evaluation helps to higher perceive traces of previous impacts, and can also have significance for totally completely different supplies.
|
|
The researchers current their findings within the journal Nature Communications (“Proof for a rosiaite-structured high-pressure silica part and its relation to lamellar amorphization in quartz”).
|
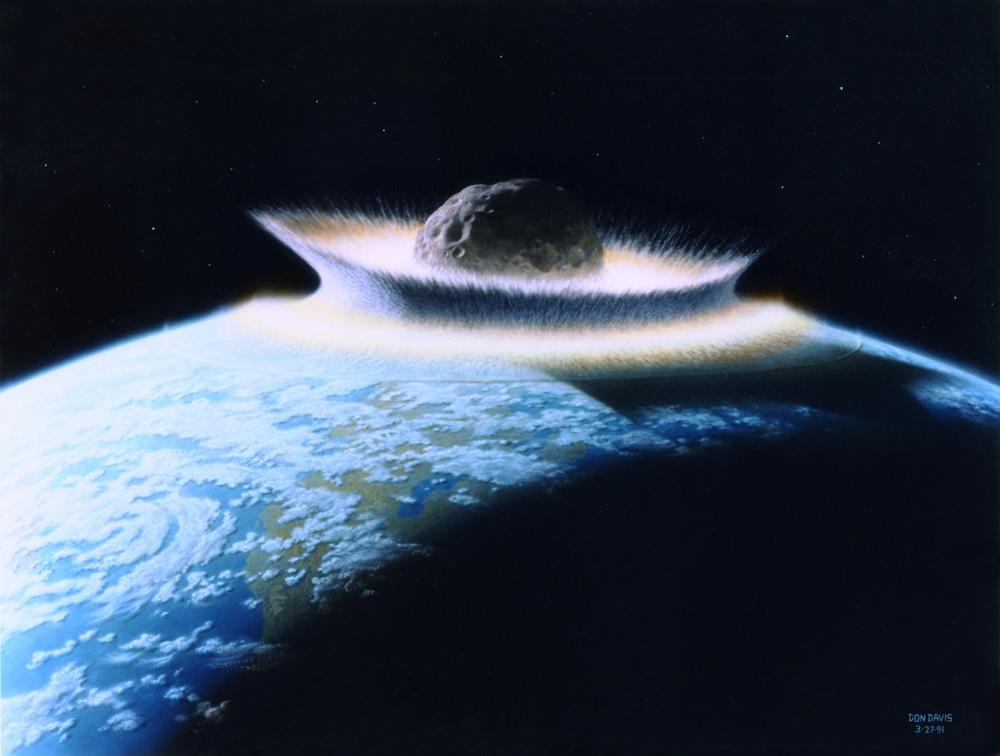 |
| Massive asteroid impacts can soften vital quantities of fabric from Earth’s crust (artist’s impression). (Picture: NASA, Don Davis)
|
Affect indicator
|
|
Asteroid impacts are catastrophic occasions that create large craters and generally soften elements of Earth’s bedrock.“ However, craters are sometimes tough to detect on Earth, as a result of erosion, weathering and plate tectonics trigger them to vanish over tens of millions of years,” Langenhorst explains. Due to this fact, minerals that bear attribute modifications as a result of pressure of the affect usually function proof of an affect.
|
|
For instance, quartz sand (which chemically is silicon dioxide, SiO2) is steadily remodeled into glass by such an affect, with the quartz grains then being crisscrossed by microscopic lamellae. This construction can solely be explored intimately beneath an electron microscope. It may be seen in materials from the comparatively current and outstanding Barringer crater in Arizona, USA, for instance.
|
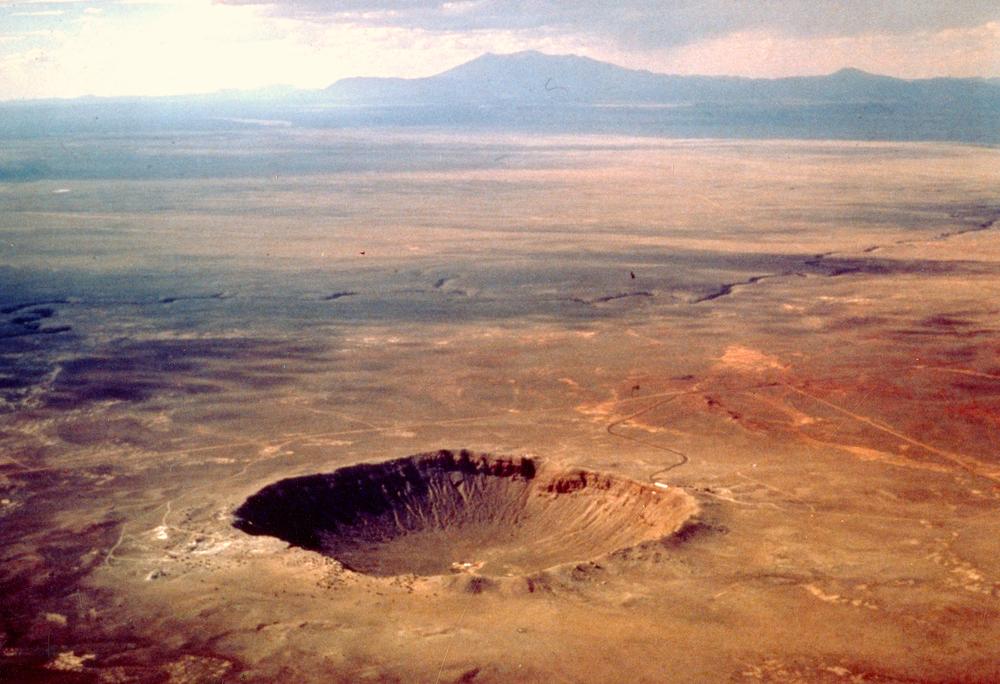 |
| Barringer crater in Arizona was shaped about 50 000 years in the past by an roughly 50-meter iron meteorite. (Picture: US Geological Survey)
|
|
“For greater than 60 years, these lamellar constructions have served as an indicator of an asteroid affect, however nobody knew till now how this construction was shaped within the first place,” Liermann says. “Now we have now solved this decades-old thriller.”
|
|
To take action, the researchers had spent years modifying and advancing strategies that permit supplies to be studied beneath excessive stress within the lab. In these experiments, samples are normally compressed between two small diamond anvils in a so-called diamond anvil cell (DAC). It permits excessive pressures – as prevalent in Earth’s inside or in an asteroid affect – to be generated in a managed method.
|
Attribute lamellae
|
|
For its experiments, the workforce used a dynamic diamond anvil cell (dDAC) during which the stress could be modified in a short time in the course of the measurement. With this system, the scientists compressed small quartz single crystals stronger and stronger, whereas shining PETRA III’s intense X-ray mild by means of them to research modifications to their crystal construction.
|
|
“The trick is to let the simulated asteroid affect proceed slowly sufficient to have the ability to observe it with the X-ray mild, however not too slowly, in order that the consequences typical of an asteroid affect can nonetheless happen,” Liermann says. Experiments on the size of seconds proved to be the fitting period.
|
|
“We noticed that at a stress of about 180,000 atmospheres, the quartz construction out of the blue remodeled right into a extra tightly packed transition construction, which we name rosiaite-like,” reviews first creator Christoph Otzen, who’s writing his doctoral thesis on these research. “On this crystal construction, the quartz shrinks by a 3rd of its quantity. The attribute lamellae kind precisely the place the quartz modifications into this so-called metastable part, which nobody has been in a position to establish in quartz earlier than us.”
|
|
Rosiaite is an oxidic mineral and the namesake for the crystal construction that’s recognized from numerous supplies. It doesn’t include silica, however is a lead antimonate (a compound of lead, antimony and oxygen).
|
Collapse into dysfunction
|
|
“The upper the stress rises, the bigger the ratio of silica with a rosiaite-like construction within the pattern,” Otzen explains. “However when the stress drops once more, the rosiaite-like lamellae don’t remodel again into the unique quartz construction, however collapse into glass lamellae with a disordered construction. We additionally see these lamellae in quartz grains from deposits of asteroid impacts.”
|
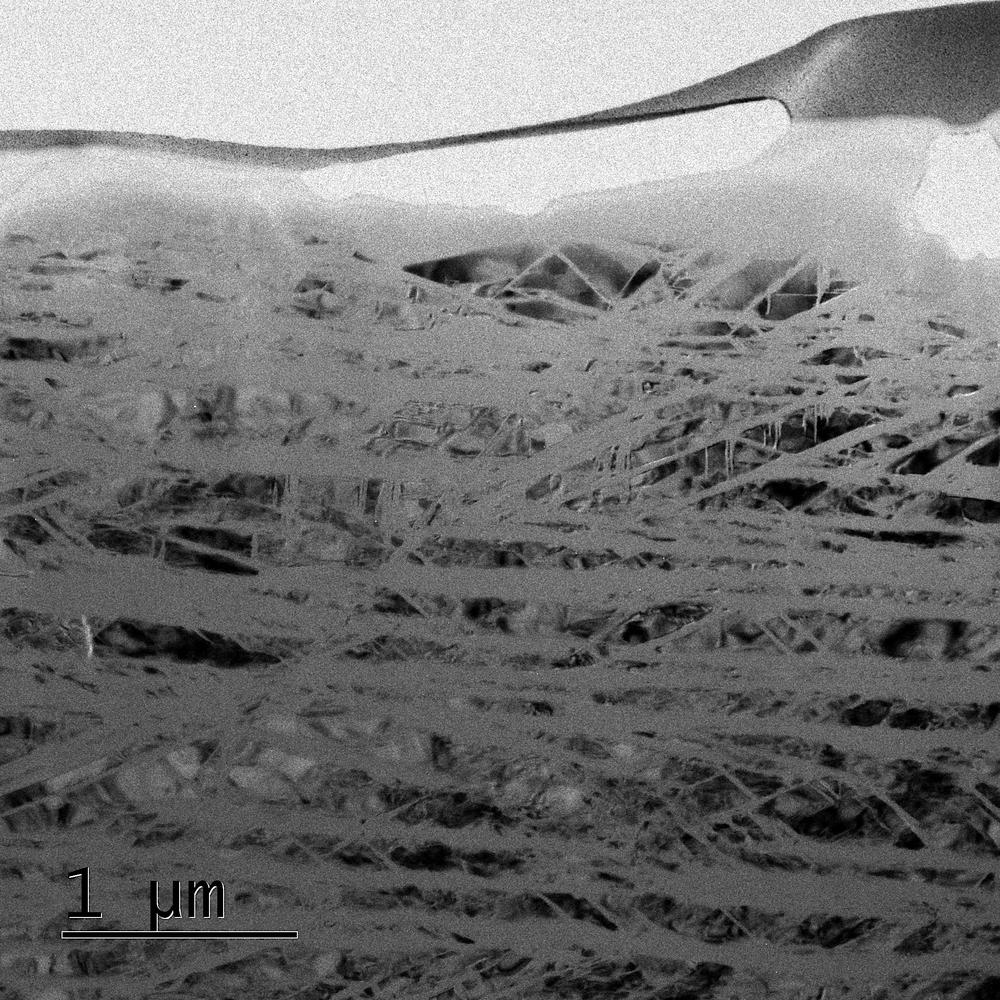 |
| The simulated asteroid affect creates tiny glass lamellae within the quartz crystals studied, solely tens of nanometers huge, that are solely seen beneath the electron microscope. (Picture: Universität Jena, Falko Langenhorst/Christoph Otzen)
|
|
Amount and orientation of the lamellae permit conclusions to be drawn concerning the affect. As an illustration, they point out how excessive the affect stress has been. “For many years, such lamellae have been used to detect and analyze asteroid impacts,” Langenhorst factors out. “However solely now can we precisely clarify and perceive their formation.
|
|
For the research, the researchers didn’t use the very best pressures technically possible. “Within the vary of the very best pressures, a lot warmth is generated that the fabric melts or vaporizes,” explains Langenhorst. “Molten materials that solidifies again into rock does not give us a lot helpful info for now. What’s essential, nonetheless, is exactly the stress vary during which minerals bear attribute modifications within the stable state, and that is what we studied on this case.”
|
Mannequin for glass formation?
|
|
The outcomes might have significance past the research of asteroid impacts. “What we noticed may very well be a mannequin research for the formation of glass in utterly completely different supplies akin to ice,” Langenhorst factors out.
|
|
“It is likely to be the generic path {that a} crystal construction transforms right into a metastable part in an intermediate step throughout speedy compression, which then transforms into the disordered glass construction. We plan to research this additional, as a result of it may very well be of nice significance for supplies analysis.”
|
|
With the deliberate transformation of PETRA III at DESY into the world’s greatest X-ray microscope, PETRA IV, such research can be much more realistically attainable sooner or later. “A 200 occasions increased X-ray depth will permit us to run these experiments 200 occasions quicker, so we are able to simulate an asteroid affect much more realistically,” says Liermann.
|





