Object-Oriented Programming, or OOPs, is a programming paradigm that implements the idea of objects in this system. It goals to supply a better resolution to real-world issues by implementing real-world entities equivalent to inheritance, abstraction, polymorphism, and so on. in programming. OOPs idea is extensively utilized in many fashionable languages like Java, Python, C++, and so on.

OOPs can be some of the essential matters for programming interviews. This text accommodates some high interview questions on the OOPs idea.
OOPs Interview Questions
1. What’s Object Oriented Programming (OOPs)?
Object Oriented Programming (also referred to as OOPs) is a programming paradigm the place the entire software program operates as a bunch of objects speaking to one another. An object is a group of information and the strategies which function on that information.
2. Why OOPs?
The primary benefit of OOP is healthier manageable code that covers the next:
- The general understanding of the software program is elevated as the space between the language spoken by builders and that spoken by customers.
- Object orientation eases upkeep by way of encapsulation. One can simply change the underlying illustration by maintaining the strategies the identical.
- The OOPs paradigm is principally helpful for comparatively huge software program.
3. What’s a Class?
A class is a constructing block of Object Oriented Applications. It’s a user-defined information sort that accommodates the information members and member features that function on the information members. It is sort of a blueprint or template of objects having frequent properties and strategies.
4. What’s an Object?
An object is an occasion of a category. Information members and strategies of a category can’t be used instantly. We have to create an object (or occasion) of the category to make use of them. In easy phrases, they’re the precise world entities which have a state and conduct.
5. What are the primary options of OOPs?
The primary function of the OOPs, also referred to as 4 pillars or fundamental ideas of OOPs are as follows:
- Encapsulation
- Information Abstraction
- Polymorphism
- Inheritance

OOPs Principal Options
6. What’s Encapsulation?
Encapsulation is the binding of information and strategies that manipulate them right into a single unit such that the delicate information is hidden from the customers
It’s applied because the processes talked about under:
- Information hiding: A language function to limit entry to members of an object. For instance, non-public and guarded members in C++.
- Bundling of information and strategies collectively: Information and strategies that function on that information are bundled collectively. For instance, the information members and member strategies that function on them are wrapped right into a single unit often called a category.

7. What’s Abstraction?
Abstraction is just like information encapsulation and is essential in OOP. It means displaying solely the required info and hiding the opposite irrelevant info from the person. Abstraction is applied utilizing courses and interfaces.

8. What’s Polymorphism?
The phrase “Polymorphism” means having many varieties. It’s the property of some code to behave in a different way for various contexts. For instance, in C++ language, we are able to outline a number of features having the identical identify however completely different working relying on the context.
9. What’s Inheritance? What’s its objective?
The concept of inheritance is easy, a category is derived from one other class and makes use of information and implementation of that different class. The category which is derived known as little one or derived or subclass and the category from which the kid class is derived known as guardian or base or superclass.
The primary objective of Inheritance is to extend code reusability. Additionally it is used to attain Runtime Polymorphism.
10. What are entry specifiers? What’s their significance in OOPs?
Entry specifiers are particular kinds of key phrases which can be used to specify or management the accessibility of entities like courses, strategies, and so forth. Non-public, Public, and Protected are examples of entry specifiers or entry modifiers.
The important thing elements of OOPs, encapsulation and information hiding, are largely achieved due to these entry specifiers.
11. What are the benefits and drawbacks of OOPs?
|
Benefits of OOPs |
Disadvantages of OOPs |
|---|---|
| OOPs offers enhanced code reusability. | The programmer needs to be well-skilled and will have glorious considering when it comes to objects as every little thing is handled as an object in OOPs. |
| The code is simpler to keep up and replace. | Correct planning is required as a result of OOPs is somewhat bit tough. |
| It offers higher information safety by proscribing information entry and avoiding pointless publicity. | OOPs idea is just not appropriate for all types of issues. |
| Quick to implement and simple to revamp leading to minimizing the complexity of an total program. | The size of the packages is way bigger compared to the procedural strategy. |
12. What different paradigms of programming exist in addition to OOPs?
The programming paradigm is referred to the method or strategy of writing a program. The programming paradigms could be labeled into the next sorts:

1. Crucial Programming Paradigm
It’s a programming paradigm that works by altering this system state by project statements. The primary focus on this paradigm is on methods to obtain the objective. The next programming paradigms come below this class:
- Procedural Programming Paradigm: This programming paradigm relies on the process name idea. Procedures, also referred to as routines or features are the essential constructing blocks of a program on this paradigm.
- Object-Oriented Programming or OOP: On this paradigm, we visualize each entity as an object and attempt to construction this system primarily based on the state and conduct of that object.
- Parallel Programming: The parallel programming paradigm is the processing of directions by dividing them into a number of smaller components and executing them concurrently.
2. Declarative Programming Paradigm
Declarative programming focuses on what’s to be executed moderately than the way it needs to be executed. On this paradigm, we categorical the logic of a computation with out contemplating its management circulate. The declarative paradigm could be additional labeled into:
- Logical Programming Paradigm: It’s primarily based on formal logic the place this system statements categorical the info and guidelines about the issue within the logical kind.
- Practical Programming Paradigm: Applications are created by making use of and composing features on this paradigm.
- Database Programming Paradigm: To handle information and knowledge organized as fields, data, and recordsdata, database programming fashions are utilized.
13. What’s the distinction between Structured Programming and Object Oriented Programming?
Structured Programming is a method that’s thought-about a precursor to OOP and normally consists of well-structured and separated modules. It’s a subset of procedural programming. The distinction between OOPs and Structured Programming is as follows:
|
Object-Oriented Programming |
Structural Programming |
|---|---|
| Programming that’s object-oriented is constructed on objects having a state and conduct. | A program’s logical construction is offered by structural programming, which divides packages into their corresponding features. |
| It follows a bottom-to-top strategy. | It follows a High-to-Down strategy. |
| Restricts the open circulate of information to licensed components solely offering higher information safety. | No restriction to the circulate of information. Anybody can entry the information. |
| Enhanced code reusability as a result of ideas of polymorphism and inheritance. | Code reusability is achieved by utilizing features and loops. |
| On this, strategies are written globally and code traces are processed one after the other i.e., Run sequentially. | On this, the strategy works dynamically, making calls as per the necessity of code for a sure time. |
| Modifying and updating the code is simpler. | Modifying the code is tough as in comparison with OOPs. |
| Information is given extra significance in OOPs. | Code is given extra significance. |
14. What are some generally used Object Oriented Programming Languages?
OOPs paradigm is among the hottest programming paradigms. It’s extensively utilized in many fashionable programming languages equivalent to:
15. What are the several types of Polymorphism?
Polymorphism could be labeled into two sorts primarily based on the time when the decision to the thing or perform is resolved. They’re as follows:
- Compile Time Polymorphism
- Runtime Polymorphism
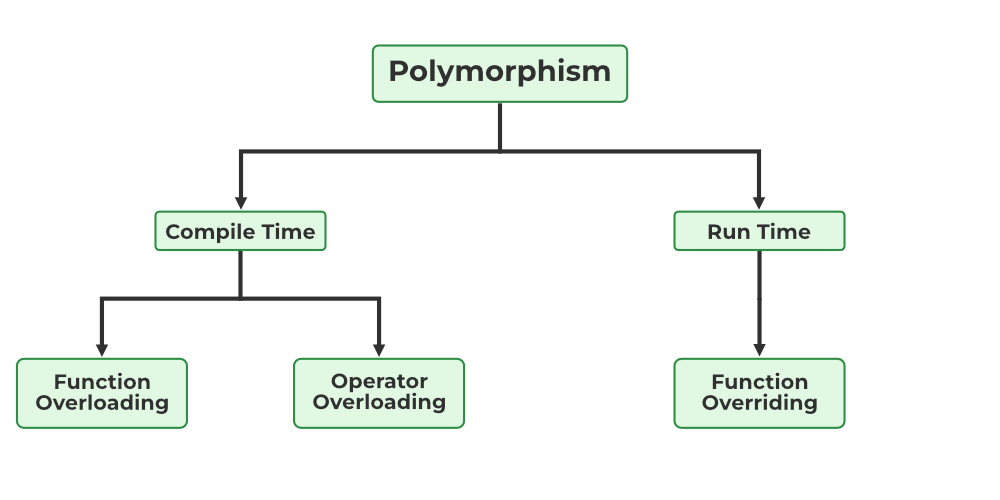
Varieties of Polymorphism
A) Compile-Time Polymorphism
Compile time polymorphism, also referred to as static polymorphism or early binding is the kind of polymorphism the place the binding of the decision to its code is finished on the compile time. Technique overloading or operator overloading are examples of compile-time polymorphism.
B) Runtime Polymorphism
Also called dynamic polymorphism or early binding, runtime polymorphism is the kind of polymorphism the place the precise implementation of the perform is decided in the course of the runtime or execution. Technique overriding is an instance of this technique.
16. What’s the distinction between overloading and overriding?
A compile-time polymorphism function known as overloading permits an entity to have quite a few implementations of the identical identify. Technique overloading and operator overloading are two examples.
Overriding is a type of runtime polymorphism the place an entity with the identical identify however a distinct implementation is executed. It’s applied with the assistance of digital features.
17. Are there any limitations on Inheritance?
Sure, there are extra challenges when you could have extra authority. Though inheritance is a really robust OOPs function, it additionally has vital drawbacks.
- Because it should go by a number of courses to be applied, inheritance takes longer to course of.
- The bottom class and the kid class, that are each engaged in inheritance, are additionally intently associated to at least one one other (known as tightly coupled). Subsequently, if modifications should be made, they could should be made in each courses on the similar time.
- Implementing inheritance may be tough as properly. Subsequently, if not applied accurately, this might end in unexpected errors or inaccurate outputs.
18. What several types of inheritance are there?
Inheritance could be labeled into 5 sorts that are as follows:

- Single Inheritance: Baby class derived instantly from the bottom class.
- A number of Inheritance: Baby class derived from a number of base courses.
- Multilevel Inheritance: Baby class derived from the category which can be derived from one other base class.
- Hierarchical Inheritance: A number of little one courses derived from a single base class.
- Hybrid Inheritance: Inheritance consisting of a number of inheritance kinds of the above specified.
19. What’s an interface?
A singular class sort often called an interface accommodates strategies however not their definitions. Inside an interface, solely technique declaration is permitted. You can not make objects utilizing an interface. As an alternative, you should put that interface into use and specify the procedures for doing so.
20. How is an summary class completely different from an interface?
Each summary courses and interfaces are particular kinds of courses that simply embrace the declaration of the strategies, not their implementation. An summary class is totally distinct from an interface, although. Following are some main variations between an summary class and an interface.
|
Summary Class |
Interface |
|---|---|
| When an summary class is inherited, nevertheless, the subclass is just not required to provide the definition of the summary technique till and except the subclass really makes use of it. | When an interface is applied, the subclass is required to specify all the interface’s strategies in addition to their implementation. |
| A category that’s summary can have each summary and non-abstract strategies. | An interface can solely have summary strategies. |
| An summary class can have closing, non-final, static and non-static variables. | The interface has solely static and closing variables. |
| Summary class doesn’t assist a number of inheritance. | An interface helps a number of inheritance. |
21. How a lot reminiscence does a category occupy?
Courses don’t use reminiscence. They merely function a template from which objects are made. Now, objects really initialize the category members and strategies when they’re created, utilizing reminiscence within the course of.
22. Is it at all times essential to create objects from class?
No. If the bottom class contains non-static strategies, an object have to be constructed. However no objects should be generated if the category contains static strategies. On this occasion, you should use the category identify to instantly name these static strategies.
23. What’s the distinction between a construction and a category in C++?
The construction can be a user-defined datatype in C++ just like the category with the next variations:
- The main distinction between a construction and a category is that in a construction, the members are set to public by default whereas in a category, members are non-public by default.
- The opposite distinction is that we use struct for declaring construction and class for declaring a category in C++.
24. What’s Constructor?
A constructor is a block of code that initializes the newly created object. A constructor resembles an occasion technique but it surely’s not a technique because it doesn’t have a return sort. It usually is the strategy having the identical identify as the category however in some languages, it would differ. For instance:
In python, a constructor is called __init__.
In C++ and Java, the constructor is called the identical as the category identify.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Java
|
|
Python3
|
|
25. What are the varied kinds of constructors in C++?
The commonest classification of constructors contains:
- Default Constructor
- Non-Parameterized Constructor
- Parameterized Constructor
- Copy Constructor
1. Default Constructor
The default constructor is a constructor that doesn’t take any arguments. It’s a non-parameterized constructor that’s robotically outlined by the compiler when no express constructor definition is offered.
It initializes the information members to their default values.
2. Non-Parameterized Constructor
It’s a user-defined constructor having no arguments or parameters.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Java
|
|
Python3
|
|
3. Parameterized Constructor
The constructors that take some arguments are often called parameterized constructors.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Java
|
|
Python3
|
|
4. Copy Constructor
A duplicate constructor is a member perform that initializes an object utilizing one other object of the identical class.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Java
|
|
In Python, we should not have built-in copy constructors like Java and C++ however we are able to make a workaround utilizing completely different strategies.
26. What’s a destructor?
A destructor is a technique that’s robotically known as when the thing is product of scope or destroyed.
In C++, the destructor identify can be the identical as the category identify however with the (~) tilde image because the prefix.
In Python, the destructor is called __del__.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Python3
|
|
In Java, the rubbish collector robotically deletes the ineffective objects so there isn’t a idea of destructor in Java. We might have used finalize() technique as a workaround for the java destructor however additionally it is deprecated since Java 9.
27. Can we overload the constructor in a category?
We will overload the constructor in a category. In actual fact, the default constructor, parameterized constructor, and replica constructor are the overloaded types of the constructor.
28. Can we overload the destructor in a category?
No. A destructor can’t be overloaded in a category. The can solely be one destructor current in a category.
29. What’s the digital perform?
A digital perform is a perform that’s used to override a technique of the guardian class within the derived class. It’s used to supply abstraction in a category.
In C++, a digital perform is said utilizing the digital key phrase,
In Java, each public, non-static, and non-final technique is a digital perform.
Python strategies are at all times digital.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Java
|
|
Python3
|
|
31. What’s pure digital perform?
A pure digital perform, also referred to as an summary perform is a member perform that doesn’t include any statements. This perform is outlined within the derived class if wanted.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Java
|
|
In Python, we obtain this utilizing @abstractmethod from the ABC (Summary Base Class) module.
30. What’s an summary class?
Typically phrases, an summary class is a category that’s meant for use for inheritance. It can’t be instantiated. An summary class can include each summary and non-abstract strategies.
In C++, an summary class is a category that accommodates at the least one pure digital perform.
In Java, an summary class is said with an summary key phrase.
Instance:
C++
|
|
Java
|
|
In Python, we use ABC (Summary Base Class) module to create an summary class.
Should Refer:


