Shoppers are those who make nearly all of consumption choices. A shopper is somebody who buys items and companies to fulfil calls for. He makes decisions in regards to the sorts of things to be purchased to fulfil his wishes. The first objective is to maximise satisfaction from the products and companies he purchases along with his earnings. To attain the best degree of satisfaction, a shopper should comply with sure guidelines or ideas since assets are restricted in nature compared to limitless calls for. The 2 fundamental approaches for finding out buyer behaviour are the Cardinal Utility method and Ordinal Utility Method.
What’s Cardinal Utility Method?
Individuals devour totally different items and companies to maximise their degree of satisfaction. To attain this, it’s required to establish the extent of satisfaction attained from a sure commodity. The Cardinal Utility Method employs the idea of “Utility” to find out the extent of satisfaction.
What’s Utility?
The attribute of a great or service that enables it to fulfil the wants of customers is comprehended as its “utility.” It’s the fulfilment—precise or anticipated—that outcomes from the consumption of a great or service. Utility is a relative idea, which means that it differs from particular person to particular person, from location to location, and from interval to interval. A utility is its means to fulfill a necessity.
Merely put, Utility is the need satisfying energy of a commodity.
It’s thought-about to be measured when it comes to cardinal numbers akin to 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. These are often called utils or items of utility. Thus, 4 utils are extra important than three utils, three utils are extra important than two utils, and so forth.
The right way to measure Utility?
In accordance with classical economics, utility will be measured equally to how one would measure one’s peak or weight. In accordance with economists, the utility will be quantified in cardinal phrases. It’s attainable to quantify the utility that a person obtains via the consumption of commodities and companies. Nonetheless, there was no standardised technique of calculating utility; so the economists got here up with a hypothetical unit of measurement known as Util.
Utils are imaginary and psychological items which are used to measure satisfaction obtained from the consumption of a sure amount of a commodity.
Let’s say you simply completed a cake and a bar of chocolate. You determine to label 15 utils as cake-derived utils. What number of utils ought to be assigned to the chocolate now? Lower than 15 utils could be given to chocolate if somebody didn’t get pleasure from it as a lot. However, if one prefers chocolate extra, then greater than 15 utils will probably be assigned.
Another technique to measure Utility
As utils fluctuate from particular person to particular person, it can’t be taken as a typical unit for measurement. Subsequently, numerous economists prompt that utility ought to be measured in financial phrases. Merely put, they prompt that utility will be measured when it comes to value or cash a shopper is keen to pay.
Within the above instance, allow us to assume that 1 util is the same as ₹1. Now, the utility derived from the consumption of cake will probably be ₹15, which is named the worth of utility when it comes to cash. The most important benefit of utilizing the financial worth of utility as a substitute of utils is that financial worth permits straightforward comparability between the worth paid for the commodity and the utility derived from it.
1. Complete Utility
Complete Utility determines the general satisfaction obtained after consuming each single unit of that commodity. It’s the complete utility derived from the consumption of all items of a commodity.
For instance, if 2 items of a commodity are consumed and the 1st unit gives 20 utils of satisfaction and the twond unit gives 14 utils of satisfaction, then the whole utility will probably be 20+ 14 utils = 34 utils. If 3rd unit of a commodity is consumed and it gives 10 utils of satisfaction, then the whole utility will probably be 20+14+10 = 44 utils.
Complete Utility will be calculated as:
TUn = U1 + U2 + U3+…………………….+ Un
The place,
TUn = Complete utility from n items of a given commodity
U1, U2, U3,……….Un = Utility derived from 1st, 2nd, 3rd,…………..nth unit
n = Variety of items consumed
2. Marginal Utility
Marginal Utility is the utility obtained from the final unit of a services or products. It refers back to the further utility on account of the consumption of a further unit of a commodity.
Within the above instance, when 3 items of a commodity present the satisfaction of 44 utils, and a pair of items of a commodity present satisfaction of 34 utils, then the marginal utility will probably be 44 – 34 = 10 utils. The extra 10 utils derived from the threerd unit are marginal utility.
MU will be calculated as:
MUn = TUn – TUn-1
The place,
MUn = Marginal utility from n items of a given commodity
TUn = Complete utility from n items of a given commodity
TUn-1 = Complete utility from n-1 items
n = Variety of items consumed
Another technique to calculate MU
MU is the change in TU attributable to the consumption of 1 further unit. MU will also be calculated when the change in items consumed is a couple of.
![]()
This ends in one other system for calculating TU.
TUn = MU1 + MU2 + MU3+…………………….+ MUn, or
TU = ∑MU
The beneath desk illustrates the estimation of MU and TU.
|
Consumption of Commodity X |
TUx |
MUX |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
50 |
50 (50 – 0 = 50) |
|
2 |
90 |
40 (90 – 50 = 40) |
|
3 |
120 |
30 (120 – 90 = 30) |
|
4 |
120 |
0 (120 – 120 = 0) |
|
5 |
100 |
-20 (100 – 120 = -20) |
The above desk reveals that:
(i) MUn = TUn – TUn-1
Marginal utility of an nth unit of a commodity =Complete utility from n items – Complete utility from (n-1) items
(ii) TU = ΣMU
= 50 + 40 + 30 + 0 + (-20)
= 100

Relationship between TU and MU
The connection between TU and MU will be defined with the assistance of the next schedule and diagram.
|
Burger |
Complete Utility |
Marginal Utility |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
0 |
– |
|
1 |
8 |
8 – 0 = 8 |
|
2 |
14 |
14 – 8 = 6 |
|
3 |
18 |
18 – 14 = 4 |
|
4 |
20 |
20 – 18 = 2 |
|
5 |
20 |
20 – 20 = 0 |
|
6 |
18 |
18 – 20 = -2 |
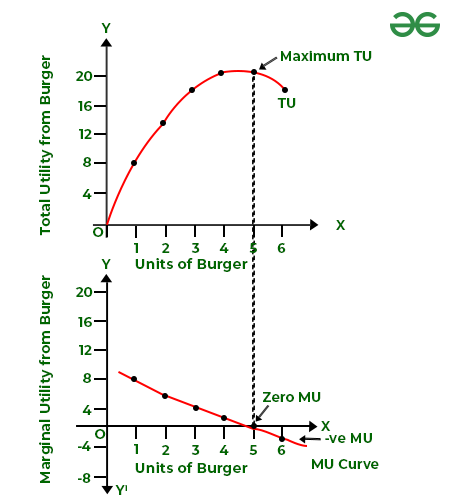
Remark:
1. TU will increase with a rise within the consumption of a commodity and so long as MU is optimistic. On this case, TU will increase until 4th burger. Until 4 burgers, TU will increase at a diminishing charge as MU from every successive burger diminishes.
2. When TU is at its most level, MU turns into zero; i.e., when the 5th burger is consumed. This level is named the level of satiety.
3. In the end, when the consumption of a commodity is elevated past the purpose of satiety, TU begins falling as MU turns into damaging.
Primary Limitation of Utility Evaluation
The elemental downside in utility evaluation is that it makes the inaccurate assumption that utility can solely be acknowledged in cardinal numbers. it implies that utils like 1, 2, and three can by no means precisely symbolize usefulness. When two issues are consumed concurrently, satisfaction will be in contrast at finest. It’s difficult to evaluate in figures. Resulting from this disadvantage, utility evaluation is proven to have minimal software in describing shopper equilibrium.
What’s Ordinal Utility Method?
This method states that utility can’t be expressed in cardinal numbers like 1,2,3, and 4, reasonably it could solely be ranked as excessive or low. The idea of cardinal utility was discarded by fashionable economists. In accordance with them, utility is a psychological expertise that can’t be quantified in absolute phrases. They imagine that customers can order totally different mixtures of products and companies to their preferences.
For instance, if a shopper consumes two items like Tea and Espresso, then he can say that:
- He prefers tea over espresso;
- He prefers espresso over tea;
- Each are equally preferable and each of them present the identical degree of satisfaction. This means that he’s detached between tea and low.


